Chandrayaan-3 Mission Overview:
- Chandrayaan-3 is a follow-on mission to Chandrayaan-2.
- Its goal is to demonstrate safe landing and roving capabilities on the lunar surface.
- The mission includes a Lander and Rover configuration.
- It will be launched by LVM3 from SDSC SHAR, Sriharikota.
- The propulsion module will transport the lander and rover to a 100 km lunar orbit.
- The propulsion module contains the SHAPE payload for studying Earth from lunar orbit.
Lander Payloads: 7. ChaSTE measures thermal conductivity and temperature.
- ILSA measures seismic activity around the landing site.
- Langmuir Probe estimates plasma density variations.
- NASA’s Laser Retroreflector Array for lunar laser ranging.
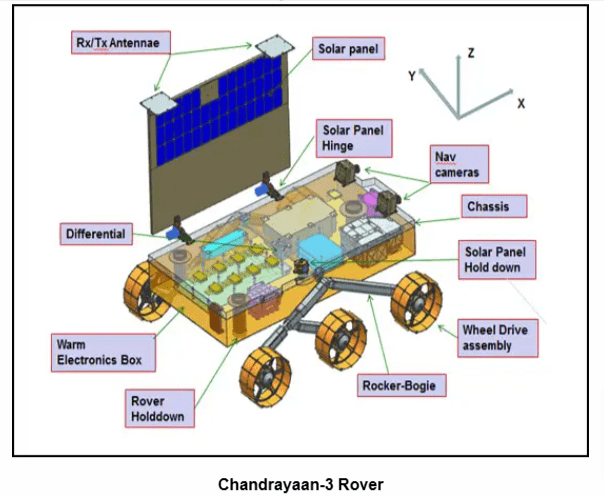
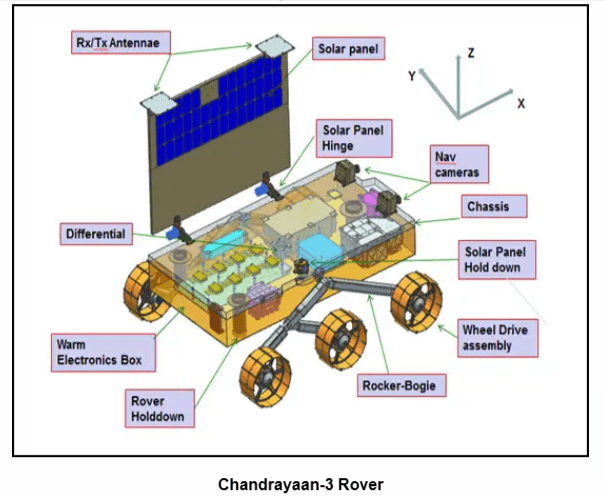
Rover Payloads: 11. APXS and LIBS perform elemental composition analysis.
- Chandrayaan-3 aims to develop and demonstrate technologies for interplanetary missions.
- The lander can soft land and deploy the rover for chemical analysis.
- Chandrayaan-3 will use LVM3 M4 launcher for placement in an elliptic parking orbit.
Mission Objectives: 15. Demonstrate safe and soft landing on the lunar surface.
- Demonstrate rover mobility on the Moon.
- Conduct in-situ scientific experiments.
Lander Advanced Technologies: 18. Altimeters: Laser and RF-based altimeters.
- Velocimeters: Laser Doppler Velocimeter and Lander Horizontal Velocity Camera.
- Inertial Measurement: Laser Gyro-based referencing and accelerometer package.
- Propulsion System: Throttleable liquid engines and attitude thrusters.
- Navigation, Guidance & Control: Powered descent trajectory design and software elements.
- Hazard Detection and Avoidance: Lander Hazard Detection & Avoidance Camera and Algorithm.
- Lander leg mechanism and performance tests.
Specifications: 25. Mission life: One lunar day (~14 Earth days).
- Landing site: 4 km x 2.4 km area.
- Mass: Propulsion Module (2148 kg), Lander Module (1752 kg including 26 kg rover).
- Power generation: Propulsion Module (758 W), Lander Module (738 W with bias), Rover (50 W).
- Communication: Propulsion and Lander Modules communicate with IDSN.
- Lander Sensors: Various sensors for navigation, altitude, velocity, and hazard detection.
Payload Objectives: 31. RAMBHA aims to measure plasma density near the lunar surface.
- ChaSTE studies thermal properties of lunar surface near polar region.
- ILSA measures lunar seismic activity and crust/mantle structure.
- LIBS provides elemental analysis, while APXS determines elemental composition of lunar soil and rocks.
- SHAPE payload for spectro-polarimetry of habitable planets.
[qsm quiz=2]